Product Description
SPROCKET 1/2'' X 5/16'' 08B SERIES SPROCKETS
| For Chain Acc.to DIN8187 ISO/R 606 | |||||
| Tooth Radius r3 | 13.0mm | ||||
| Radius Width C | 1.3mm | ||||
| Tooth Width b1 | 7.0mm | ||||
| Tooth Width B1 | 7.2mm | ||||
| Tooth Width B2 | 21.0mm | ||||
| Tooth Width B3 | 34.9mm | ||||
| 08B SERIES ROLLER CHAINS | |||||
| Pitch | 12.7 mm | ||||
| Internal Width | 7.75 mm | ||||
| Roller Diameter | 8.51 mm | ||||
| Z | de | dp | SIMPLEX | DUPLEX | TRIPLEX |
| D1 | D2 | D3 | |||
| 8 | 37.2 | 33.18 | 8 | 10 | 10 |
| 9 | 41.0 | 37.13 | 8 | 10 | 10 |
| 10 | 45.2 | 41.10 | 8 | 10 | 10 |
| 11 | 48.7 | 45.07 | 10 | 10 | 12 |
| 12 | 53.0 | 49.07 | 10 | 10 | 12 |
| 13 | 57.4 | 53.06 | 10 | 10 | 12 |
| 14 | 61.8 | 57.07 | 10 | 10 | 12 |
| 15 | 65.5 | 61.09 | 10 | 10 | 12 |
| 16 | 69.5 | 65.10 | 10 | 12 | 16 |
| 17 | 73.6 | 69.11 | 10 | 12 | 16 |
| 18 | 77.8 | 73.14 | 10 | 12 | 16 |
| 19 | 81.7 | 77.16 | 10 | 12 | 16 |
| 20 | 85.8 | 81.19 | 10 | 12 | 16 |
| 21 | 89.7 | 85.22 | 12 | 16 | 16 |
| 22 | 93.8 | 89.24 | 12 | 16 | 16 |
| 23 | 98.2 | 93.27 | 12 | 16 | 16 |
| 24 | 101.8 | 97.29 | 12 | 16 | 16 |
| 25 | 105.8 | 101.33 | 12 | 16 | 16 |
| 26 | 110.0 | 105.36 | 16 | 16 | 16 |
| 27 | 114.0 | 109.40 | 16 | 16 | 16 |
| 28 | 118.0 | 113.42 | 16 | 16 | 16 |
| 29 | 122.0 | 117.46 | 16 | 16 | 16 |
| 30 | 126.1 | 121.50 | 16 | 16 | 16 |
| 31 | 130.2 | 125.54 | 16 | 16 | 20 |
| 32 | 134.3 | 129.56 | 16 | 16 | 20 |
| 33 | 138.4 | 133.60 | 16 | 16 | 20 |
| 34 | 142.6 | 137.64 | 16 | 16 | 20 |
| 35 | 146.7 | 141.68 | 16 | 16 | 20 |
| 36 | 151.0 | 145.72 | 16 | 20 | 20 |
| 37 | 154.6 | 149.76 | 16 | 20 | 20 |
| 38 | 158.6 | 153.80 | 16 | 20 | 20 |
| 39 | 162.7 | 157.83 | 16 | 20 | 20 |
| 40 | 166.8 | 161.87 | 16 | 20 | 20 |
| 41 | 171.4 | 165.91 | 20 | 20 | 25 |
| 42 | 175.4 | 169.94 | 20 | 20 | 25 |
| 43 | 179.7 | 173.98 | 20 | 20 | 25 |
| 44 | 183.8 | 178.02 | 20 | 20 | 25 |
| 45 | 188.0 | 182.07 | 20 | 20 | 25 |
| 46 | 192.1 | 186.10 | 20 | 20 | 25 |
| 47 | 196.2 | 190.14 | 20 | 20 | 25 |
| 48 | 200.3 | 194.18 | 20 | 20 | 25 |
| 49 | 204.3 | 198.22 | 20 | 20 | 25 |
| 50 | 208.3 | 202.26 | 20 | 20 | 25 |
| 51 | 212.1 | 206.30 | 20 | 25 | 25 |
| 52 | 216.1 | 210.34 | 20 | 25 | 25 |
| 53 | 220.2 | 214.37 | 20 | 25 | 25 |
| 54 | 224.1 | 218.43 | 20 | 25 | 25 |
| 55 | 228.1 | 222.46 | 20 | 25 | 25 |
| 56 | 232.2 | 226.50 | 20 | 25 | 25 |
| 57 | 236.4 | 230.54 | 20 | 25 | 25 |
| 58 | 240.5 | 234.58 | 20 | 25 | 25 |
| 59 | 244.5 | 238.62 | 20 | 25 | 25 |
| 60 | 248.6 | 242.66 | 20 | 25 | 25 |
| 62 | 256.9 | 250.74 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| 64 | 265.1 | 258.82 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| 65 | 269.0 | 262.86 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| 66 | 273.0 | 266.91 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| 68 | 281.0 | 274.99 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| 70 | 289.0 | 283.07 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| 72 | 297.2 | 291.15 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| 75 | 309.2 | 303.28 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| 76 | 313.2 | 307.32 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| 78 | 321.4 | 315.40 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| 80 | 329.4 | 323.49 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| 85 | 349.0 | 343.69 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| 90 | 369.9 | 363.90 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| 95 | 390.1 | 384.11 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| 100 | 410.3 | 404.32 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| 110 | 450.7 | 444.74 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| 114 | 466.9 | 460.91 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| 120 | 491.2 | 485.16 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| 125 | 511.3 | 505.37 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
BASIC INFO.
|
Type: |
Simplex, Duplex, Triplex |
|
Sprocket Model: |
3/8",1/2",5/8",3/4",1",1.25",1.50",1.75",2.00",2.25",2.00",2.25",2.50", 3" |
|
Teeth Number: |
9-100 |
|
Standard: |
ANSI , JIS, DIN, ISO |
|
Material: |
1571, 1045, SS304 , SS316; As Per User Request. |
|
Performance Treatment: |
Carburizing, High Frequency Treatment, Hardening and Tempering, Nitriding |
|
Surface Treatment: |
Black of Oxidation, Zincing, Nickelage. |
| Characteristic | Fire Resistant, Oil Resistant, Heat Resistant, CZPT resistance, Oxidative resistance, Corrosion resistance, etc |
| Design criterion | ISO DIN ANSI & Customer Drawings |
| Application | Industrial transmission equipment |
| Package | Wooden Case / Container and pallet, or made-to-order |
|
Certification: |
ISO9001 SGS |
|
Quality Inspection: |
Self-check and Final-check |
|
Sample: |
ODM&OEM, Trial Order Available and Welcome |
| Advantage | Quality first, Service first, Competitive price, Fast delivery |
| Delivery Time | 10 days for samples. 15 days for official order. |
INSTALLATION AND USING
The chain spocket, as a drive or deflection for chains, has pockets to hold the chain links with a D-profile cross section with flat side surfaces parallel to the centre plane of the chain links, and outer surfaces at right angles to the chain link centre plane. The chain links are pressed firmly against the outer surfaces and each of the side surfaces by the angled laying surfaces at the base of the pockets, and also the support surfaces of the wheel body together with the end sides of the webs formed by the leading and trailing walls of the pocket.
NOTICE
When fitting new chainwheels it is very important that a new chain is fitted at the same time, and vice versa. Using an old chain with new sprockets, or a new chain with old sprockets will cause rapid wear.
It is important if you are installing the chainwheels yourself to have the factory service manual specific to your model. Our chainwheels are made to be a direct replacement for your OEM chainwheels and as such, the installation should be performed according to your models service manual.
During use a chain will stretch (i.e. the pins will wear causing extension of the chain). Using a chain which has been stretched more than the above maximum allowance causes the chain to ride up the teeth of the sprocket. This causes damage to the tips of the chainwheels teeth, as the force transmitted by the chain is transmitted entirely through the top of the tooth, rather than the whole tooth. This results in severe wearing of the chainwheel.
FOR CHAIN STHangZhouRDS
Standards organizations (such as ANSI and ISO) maintain standards for design, dimensions, and interchangeability of transmission chains. For example, the following Table shows data from ANSI standard B29.1-2011 (Precision Power Transmission Roller Chains, Attachments, and Sprockets) developed by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME). See the references[8][9][10] for additional information.
ASME/ANSI B29.1-2011 Roller Chain Standard SizesSizePitchMaximum Roller DiameterMinimum Ultimate Tensile StrengthMeasuring Load25
| ASME/ANSI B29.1-2011 Roller Chain Standard Sizes | ||||
| Size | Pitch | Maximum Roller Diameter | Minimum Ultimate Tensile Strength | Measuring Load |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | 0.250 in (6.35 mm) | 0.130 in (3.30 mm) | 780 lb (350 kg) | 18 lb (8.2 kg) |
| 35 | 0.375 in (9.53 mm) | 0.200 in (5.08 mm) | 1,760 lb (800 kg) | 18 lb (8.2 kg) |
| 41 | 0.500 in (12.70 mm) | 0.306 in (7.77 mm) | 1,500 lb (680 kg) | 18 lb (8.2 kg) |
| 40 | 0.500 in (12.70 mm) | 0.312 in (7.92 mm) | 3,125 lb (1,417 kg) | 31 lb (14 kg) |
| 50 | 0.625 in (15.88 mm) | 0.400 in (10.16 mm) | 4,880 lb (2,210 kg) | 49 lb (22 kg) |
| 60 | 0.750 in (19.05 mm) | 0.469 in (11.91 mm) | 7,030 lb (3,190 kg) | 70 lb (32 kg) |
| 80 | 1.000 in (25.40 mm) | 0.625 in (15.88 mm) | 12,500 lb (5,700 kg) | 125 lb (57 kg) |
| 100 | 1.250 in (31.75 mm) | 0.750 in (19.05 mm) | 19,531 lb (8,859 kg) | 195 lb (88 kg) |
| 120 | 1.500 in (38.10 mm) | 0.875 in (22.23 mm) | 28,125 lb (12,757 kg) | 281 lb (127 kg) |
| 140 | 1.750 in (44.45 mm) | 1.000 in (25.40 mm) | 38,280 lb (17,360 kg) | 383 lb (174 kg) |
| 160 | 2.000 in (50.80 mm) | 1.125 in (28.58 mm) | 50,000 lb (23,000 kg) | 500 lb (230 kg) |
| 180 | 2.250 in (57.15 mm) | 1.460 in (37.08 mm) | 63,280 lb (28,700 kg) | 633 lb (287 kg) |
| 200 | 2.500 in (63.50 mm) | 1.562 in (39.67 mm) | 78,175 lb (35,460 kg) | 781 lb (354 kg) |
| 240 | 3.000 in (76.20 mm) | 1.875 in (47.63 mm) | 112,500 lb (51,000 kg) | 1,000 lb (450 kg |
For mnemonic purposes, below is another presentation of key dimensions from the same standard, expressed in fractions of an inch (which was part of the thinking behind the choice of preferred numbers in the ANSI standard):
| Pitch (inches) | Pitch expressed in eighths |
ANSI standard chain number |
Width (inches) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1⁄4 | 2⁄8 | 25 | 1⁄8 |
| 3⁄8 | 3⁄8 | 35 | 3⁄16 |
| 1⁄2 | 4⁄8 | 41 | 1⁄4 |
| 1⁄2 | 4⁄8 | 40 | 5⁄16 |
| 5⁄8 | 5⁄8 | 50 | 3⁄8 |
| 3⁄4 | 6⁄8 | 60 | 1⁄2 |
| 1 | 8⁄8 | 80 | 5⁄8 |
Notes:
1. The pitch is the distance between roller centers. The width is the distance between the link plates (i.e. slightly more than the roller width to allow for clearance).
2. The right-hand digit of the standard denotes 0 = normal chain, 1 = lightweight chain, 5 = rollerless bushing chain.
3. The left-hand digit denotes the number of eighths of an inch that make up the pitch.
4. An "H" following the standard number denotes heavyweight chain. A hyphenated number following the standard number denotes double-strand (2), triple-strand (3), and so on. Thus 60H-3 denotes number 60 heavyweight triple-strand chain.
A typical bicycle chain (for derailleur gears) uses narrow 1⁄2-inch-pitch chain. The width of the chain is variable, and does not affect the load capacity. The more sprockets at the rear wheel (historically 3-6, nowadays 7-12 sprockets), the narrower the chain. Chains are sold according to the number of speeds they are designed to work with, for example, "10 speed chain". Hub gear or single speed bicycles use 1/2" x 1/8" chains, where 1/8" refers to the maximum thickness of a sprocket that can be used with the chain.
Typically chains with parallel shaped links have an even number of links, with each narrow link followed by a broad one. Chains built up with a uniform type of link, narrow at 1 and broad at the other end, can be made with an odd number of links, which can be an advantage to adapt to a special chainwheel-distance; on the other side such a chain tends to be not so strong.
Roller chains made using ISO standard are sometimes called as isochains.
WHY CHOOSE US
1. Reliable Quality Assurance System
2. Cutting-Edge Computer-Controlled CNC Machines
3. Bespoke Solutions from Highly Experienced Specialists
4. Customization and OEM Available for Specific Application
5. Extensive Inventory of Spare Parts and Accessories
6. Well-Developed CZPT Marketing Network
7. Efficient After-Sale Service System
The 219 sets of advanced automatic production equipment provide guarantees for high product quality. The 167 engineers and technicians with senior professional titles can design and develop products to meet the exact demands of customers, and OEM customizations are also available with us. Our sound global service network can provide customers with timely after-sales technical services.
We are not just a manufacturer and supplier, but also an industry consultant. We work pro-actively with you to offer expert advice and product recommendations in order to end up with a most cost effective product available for your specific application. The clients we serve CZPT range from end users to distributors and OEMs. Our OEM replacements can be substituted wherever necessary and suitable for both repair and new assemblies.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(",").forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Standard Or Nonstandard: | Nonstandard |
|---|---|
| Application: | Motor, Electric Cars, Motorcycle, Machinery, Marine, Toy, Agricultural Machinery, Car, Motor, Electric Cars, Motorcycle, Machinery, Marine, Toy, Agricultural Machinery, Car |
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface, Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Samples: |
US$ 0/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
| Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

Can sprocket gears be used for vertical power transmission?
Yes, sprocket gears can be used for vertical power transmission in certain applications. Vertical power transmission involves transferring rotational power between two shafts that are oriented vertically, with one shaft positioned above the other. In such cases, sprocket gears, also known as chain sprockets when used with chains, can offer an efficient and reliable solution for transmitting power.
The main advantage of using sprocket gears for vertical power transmission is their ability to maintain a positive engagement with the chain, ensuring a consistent and smooth transfer of power. This positive engagement is particularly beneficial in vertical applications where gravity can potentially cause other types of gears, such as spur gears or bevel gears, to disengage or produce excessive wear.
Sprocket gears are commonly employed in vertical power transmission systems in various industries, including manufacturing, material handling, and construction. Examples of vertical power transmission applications using sprocket gears include:
1. Vertical Conveyor Systems: Sprocket gears, in combination with conveyor chains, are often used to transport materials vertically between different levels of a facility.
2. Elevators: Sprocket gears and chains are utilized in elevator systems to lift and lower the elevator car in buildings or industrial settings.
3. Vertical Lifts: Sprocket gears play a crucial role in vertical lift systems that move heavy loads between floors or levels.
4. Agricultural Equipment: Sprocket gears are used in vertical power transmission systems of agricultural machinery, such as grain elevators.
When implementing sprocket gears for vertical power transmission, it is essential to consider the load, speed, torque requirements, and system dynamics to ensure safe and efficient operation. Additionally, proper lubrication and regular maintenance are crucial for maximizing the lifespan and performance of the sprocket gear system.
Overall, sprocket gears offer a reliable and versatile solution for vertical power transmission, making them a popular choice in numerous industrial and commercial applications.

How do I prevent chain elongation in a sprocket gear system?
Preventing chain elongation is essential to maintain the efficiency and longevity of a sprocket gear system. Chain elongation occurs over time due to wear and stretch in the chain, leading to a change in pitch length and improper engagement with the sprocket teeth. Here are some measures to prevent chain elongation:
1. Proper Lubrication: Regular and adequate lubrication of the chain is crucial to reduce friction and wear between the chain's components. Lubricants also help prevent corrosion and reduce the chances of chain elongation.
2. Correct Tension: Maintaining the correct chain tension is vital to prevent excessive stress and elongation. Too much tension can accelerate wear, while too little tension can lead to slippage and increased elongation. Follow the manufacturer's guidelines for proper tensioning.
3. Quality Chain: Invest in high-quality chains that are designed to resist elongation and offer better wear resistance. High-strength chains with heat-treated components are more resistant to elongation.
4. Proper Alignment: Ensure the sprockets are properly aligned to minimize lateral forces on the chain. Misalignment can cause uneven wear and accelerated elongation.
5. Regular Inspection: Perform routine inspections of the sprocket gear system to check for signs of wear, elongation, or any other issues. Address any problems promptly to prevent further damage.
6. Replace Worn Components: As the chain and sprockets wear over time, replace them when they reach their wear limits. Continuing to use worn components can accelerate elongation and lead to premature failure.
7. Avoid Overloading: Operating the sprocket gear system within its designed load capacity will help minimize stress on the chain, reducing the chances of elongation.
8. Environmental Considerations: In harsh or abrasive environments, protective measures like covers or guards can help prevent contaminants from accelerating chain wear and elongation.
By implementing these preventive measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of chain elongation and ensure a longer and more reliable service life for your sprocket gear system.

What are the different types of sprocket gears and their applications?
Sprocket gears come in various types, each designed for specific applications based on their unique characteristics. Here are some of the different types of sprocket gears and their applications:
- 1. Plain Sprocket: Plain sprockets are the most basic type, consisting of a wheel with evenly spaced teeth. They are commonly used in simple power transmission systems and light-duty applications where precise timing is not critical.
- 2. Idler Sprocket: Idler sprockets are used to guide and tension the chain in a sprocket system. They do not connect directly to a power source but play a crucial role in maintaining proper chain tension and alignment.
- 3. Roller Chain Sprocket: Roller chain sprockets are designed to work with roller chains, which have rollers that engage with the sprocket teeth. They are widely used in applications like bicycles, motorcycles, industrial machinery, and conveyor systems.
- 4. Silent Chain Sprocket: Silent chain sprockets, also known as inverted-tooth chain sprockets, are used with silent chains. These sprockets have specially shaped teeth that engage smoothly with the chain, resulting in quieter operation.
- 5. Engineering Class Sprocket: Engineering class sprockets are heavy-duty sprockets used in industrial applications like construction equipment, mining machinery, and agricultural machinery. They are designed to withstand high loads and harsh operating conditions.
- 6. Taper-Lock Sprocket: Taper-lock sprockets have a tapered bore and are mounted on shafts using a locking bushing. They provide a secure and easy-to-install connection and are commonly used in power transmission systems.
- 7. Rack and Pinion: While not a traditional sprocket gear, rack and pinion systems use a linear rack with teeth that mesh with a pinion gear. This combination is used in applications where rotational motion needs to be translated into linear motion, such as in steering systems and CNC machines.
The choice of sprocket gear depends on factors such as the type of chain or belt used, the desired gear ratio, the amount of load the system will handle, and the specific requirements of the application. Each type of sprocket gear offers unique advantages and is tailored to meet the needs of different industries and machinery.


editor by Dream 2024-05-15
China Best Sales Chain Wheel Transmission Belt Industrial Automatic Gear Box Conveyor Parts Roller Chains Sprocket Wheel Gear
Product Description
SPROCKET 1/2'' X 5/16'' 08B SERIES SPROCKETS
| For Chain Acc.to DIN8187 ISO/R 606 | |||||
| Tooth Radius r3 | 13.0mm | ||||
| Radius Width C | 1.3mm | ||||
| Tooth Width b1 | 7.0mm | ||||
| Tooth Width B1 | 7.2mm | ||||
| Tooth Width B2 | 21.0mm | ||||
| Tooth Width B3 | 34.9mm | ||||
| 08B SERIES ROLLER CHAINS | |||||
| Pitch | 12.7 mm | ||||
| Internal Width | 7.75 mm | ||||
| Roller Diameter | 8.51 mm | ||||
| Z | de | dp | SIMPLEX | DUPLEX | TRIPLEX |
| D1 | D2 | D3 | |||
| 8 | 37.2 | 33.18 | 8 | 10 | 10 |
| 9 | 41.0 | 37.13 | 8 | 10 | 10 |
| 10 | 45.2 | 41.10 | 8 | 10 | 10 |
| 11 | 48.7 | 45.07 | 10 | 10 | 12 |
| 12 | 53.0 | 49.07 | 10 | 10 | 12 |
| 13 | 57.4 | 53.06 | 10 | 10 | 12 |
| 14 | 61.8 | 57.07 | 10 | 10 | 12 |
| 15 | 65.5 | 61.09 | 10 | 10 | 12 |
| 16 | 69.5 | 65.10 | 10 | 12 | 16 |
| 17 | 73.6 | 69.11 | 10 | 12 | 16 |
| 18 | 77.8 | 73.14 | 10 | 12 | 16 |
| 19 | 81.7 | 77.16 | 10 | 12 | 16 |
| 20 | 85.8 | 81.19 | 10 | 12 | 16 |
| 21 | 89.7 | 85.22 | 12 | 16 | 16 |
| 22 | 93.8 | 89.24 | 12 | 16 | 16 |
| 23 | 98.2 | 93.27 | 12 | 16 | 16 |
| 24 | 101.8 | 97.29 | 12 | 16 | 16 |
| 25 | 105.8 | 101.33 | 12 | 16 | 16 |
| 26 | 110.0 | 105.36 | 16 | 16 | 16 |
| 27 | 114.0 | 109.40 | 16 | 16 | 16 |
| 28 | 118.0 | 113.42 | 16 | 16 | 16 |
| 29 | 122.0 | 117.46 | 16 | 16 | 16 |
| 30 | 126.1 | 121.50 | 16 | 16 | 16 |
| 31 | 130.2 | 125.54 | 16 | 16 | 20 |
| 32 | 134.3 | 129.56 | 16 | 16 | 20 |
| 33 | 138.4 | 133.60 | 16 | 16 | 20 |
| 34 | 142.6 | 137.64 | 16 | 16 | 20 |
| 35 | 146.7 | 141.68 | 16 | 16 | 20 |
| 36 | 151.0 | 145.72 | 16 | 20 | 20 |
| 37 | 154.6 | 149.76 | 16 | 20 | 20 |
| 38 | 158.6 | 153.80 | 16 | 20 | 20 |
| 39 | 162.7 | 157.83 | 16 | 20 | 20 |
| 40 | 166.8 | 161.87 | 16 | 20 | 20 |
| 41 | 171.4 | 165.91 | 20 | 20 | 25 |
| 42 | 175.4 | 169.94 | 20 | 20 | 25 |
| 43 | 179.7 | 173.98 | 20 | 20 | 25 |
| 44 | 183.8 | 178.02 | 20 | 20 | 25 |
| 45 | 188.0 | 182.07 | 20 | 20 | 25 |
| 46 | 192.1 | 186.10 | 20 | 20 | 25 |
| 47 | 196.2 | 190.14 | 20 | 20 | 25 |
| 48 | 200.3 | 194.18 | 20 | 20 | 25 |
| 49 | 204.3 | 198.22 | 20 | 20 | 25 |
| 50 | 208.3 | 202.26 | 20 | 20 | 25 |
| 51 | 212.1 | 206.30 | 20 | 25 | 25 |
| 52 | 216.1 | 210.34 | 20 | 25 | 25 |
| 53 | 220.2 | 214.37 | 20 | 25 | 25 |
| 54 | 224.1 | 218.43 | 20 | 25 | 25 |
| 55 | 228.1 | 222.46 | 20 | 25 | 25 |
| 56 | 232.2 | 226.50 | 20 | 25 | 25 |
| 57 | 236.4 | 230.54 | 20 | 25 | 25 |
| 58 | 240.5 | 234.58 | 20 | 25 | 25 |
| 59 | 244.5 | 238.62 | 20 | 25 | 25 |
| 60 | 248.6 | 242.66 | 20 | 25 | 25 |
| 62 | 256.9 | 250.74 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| 64 | 265.1 | 258.82 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| 65 | 269.0 | 262.86 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| 66 | 273.0 | 266.91 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| 68 | 281.0 | 274.99 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| 70 | 289.0 | 283.07 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| 72 | 297.2 | 291.15 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| 75 | 309.2 | 303.28 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| 76 | 313.2 | 307.32 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| 78 | 321.4 | 315.40 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| 80 | 329.4 | 323.49 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| 85 | 349.0 | 343.69 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| 90 | 369.9 | 363.90 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| 95 | 390.1 | 384.11 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| 100 | 410.3 | 404.32 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| 110 | 450.7 | 444.74 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| 114 | 466.9 | 460.91 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| 120 | 491.2 | 485.16 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| 125 | 511.3 | 505.37 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
BASIC INFO.
|
Type: |
Simplex, Duplex, Triplex |
|
Sprocket Model: |
3/8",1/2",5/8",3/4",1",1.25",1.50",1.75",2.00",2.25",2.00",2.25",2.50", 3" |
|
Teeth Number: |
9-100 |
|
Standard: |
ANSI , JIS, DIN, ISO |
|
Material: |
1571, 1045, SS304 , SS316; As Per User Request. |
|
Performance Treatment: |
Carburizing, High Frequency Treatment, Hardening and Tempering, Nitriding |
|
Surface Treatment: |
Black of Oxidation, Zincing, Nickelage. |
| Characteristic | Fire Resistant, Oil Resistant, Heat Resistant, CZPT resistance, Oxidative resistance, Corrosion resistance, etc |
| Design criterion | ISO DIN ANSI & Customer Drawings |
| Application | Industrial transmission equipment |
| Package | Wooden Case / Container and pallet, or made-to-order |
|
Certification: |
ISO9001 SGS |
|
Quality Inspection: |
Self-check and Final-check |
|
Sample: |
ODM&OEM, Trial Order Available and Welcome |
| Advantage | Quality first, Service first, Competitive price, Fast delivery |
| Delivery Time | 10 days for samples. 15 days for official order. |
INSTALLATION AND USING
The chain spocket, as a drive or deflection for chains, has pockets to hold the chain links with a D-profile cross section with flat side surfaces parallel to the centre plane of the chain links, and outer surfaces at right angles to the chain link centre plane. The chain links are pressed firmly against the outer surfaces and each of the side surfaces by the angled laying surfaces at the base of the pockets, and also the support surfaces of the wheel body together with the end sides of the webs formed by the leading and trailing walls of the pocket.
NOTICE
When fitting new chainwheels it is very important that a new chain is fitted at the same time, and vice versa. Using an old chain with new sprockets, or a new chain with old sprockets will cause rapid wear.
It is important if you are installing the chainwheels yourself to have the factory service manual specific to your model. Our chainwheels are made to be a direct replacement for your OEM chainwheels and as such, the installation should be performed according to your models service manual.
During use a chain will stretch (i.e. the pins will wear causing extension of the chain). Using a chain which has been stretched more than the above maximum allowance causes the chain to ride up the teeth of the sprocket. This causes damage to the tips of the chainwheels teeth, as the force transmitted by the chain is transmitted entirely through the top of the tooth, rather than the whole tooth. This results in severe wearing of the chainwheel.
FOR CHAIN STHangZhouRDS
Standards organizations (such as ANSI and ISO) maintain standards for design, dimensions, and interchangeability of transmission chains. For example, the following Table shows data from ANSI standard B29.1-2011 (Precision Power Transmission Roller Chains, Attachments, and Sprockets) developed by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME). See the references[8][9][10] for additional information.
ASME/ANSI B29.1-2011 Roller Chain Standard SizesSizePitchMaximum Roller DiameterMinimum Ultimate Tensile StrengthMeasuring Load25
| ASME/ANSI B29.1-2011 Roller Chain Standard Sizes | ||||
| Size | Pitch | Maximum Roller Diameter | Minimum Ultimate Tensile Strength | Measuring Load |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | 0.250 in (6.35 mm) | 0.130 in (3.30 mm) | 780 lb (350 kg) | 18 lb (8.2 kg) |
| 35 | 0.375 in (9.53 mm) | 0.200 in (5.08 mm) | 1,760 lb (800 kg) | 18 lb (8.2 kg) |
| 41 | 0.500 in (12.70 mm) | 0.306 in (7.77 mm) | 1,500 lb (680 kg) | 18 lb (8.2 kg) |
| 40 | 0.500 in (12.70 mm) | 0.312 in (7.92 mm) | 3,125 lb (1,417 kg) | 31 lb (14 kg) |
| 50 | 0.625 in (15.88 mm) | 0.400 in (10.16 mm) | 4,880 lb (2,210 kg) | 49 lb (22 kg) |
| 60 | 0.750 in (19.05 mm) | 0.469 in (11.91 mm) | 7,030 lb (3,190 kg) | 70 lb (32 kg) |
| 80 | 1.000 in (25.40 mm) | 0.625 in (15.88 mm) | 12,500 lb (5,700 kg) | 125 lb (57 kg) |
| 100 | 1.250 in (31.75 mm) | 0.750 in (19.05 mm) | 19,531 lb (8,859 kg) | 195 lb (88 kg) |
| 120 | 1.500 in (38.10 mm) | 0.875 in (22.23 mm) | 28,125 lb (12,757 kg) | 281 lb (127 kg) |
| 140 | 1.750 in (44.45 mm) | 1.000 in (25.40 mm) | 38,280 lb (17,360 kg) | 383 lb (174 kg) |
| 160 | 2.000 in (50.80 mm) | 1.125 in (28.58 mm) | 50,000 lb (23,000 kg) | 500 lb (230 kg) |
| 180 | 2.250 in (57.15 mm) | 1.460 in (37.08 mm) | 63,280 lb (28,700 kg) | 633 lb (287 kg) |
| 200 | 2.500 in (63.50 mm) | 1.562 in (39.67 mm) | 78,175 lb (35,460 kg) | 781 lb (354 kg) |
| 240 | 3.000 in (76.20 mm) | 1.875 in (47.63 mm) | 112,500 lb (51,000 kg) | 1,000 lb (450 kg |
For mnemonic purposes, below is another presentation of key dimensions from the same standard, expressed in fractions of an inch (which was part of the thinking behind the choice of preferred numbers in the ANSI standard):
| Pitch (inches) | Pitch expressed in eighths |
ANSI standard chain number |
Width (inches) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1⁄4 | 2⁄8 | 25 | 1⁄8 |
| 3⁄8 | 3⁄8 | 35 | 3⁄16 |
| 1⁄2 | 4⁄8 | 41 | 1⁄4 |
| 1⁄2 | 4⁄8 | 40 | 5⁄16 |
| 5⁄8 | 5⁄8 | 50 | 3⁄8 |
| 3⁄4 | 6⁄8 | 60 | 1⁄2 |
| 1 | 8⁄8 | 80 | 5⁄8 |
Notes:
1. The pitch is the distance between roller centers. The width is the distance between the link plates (i.e. slightly more than the roller width to allow for clearance).
2. The right-hand digit of the standard denotes 0 = normal chain, 1 = lightweight chain, 5 = rollerless bushing chain.
3. The left-hand digit denotes the number of eighths of an inch that make up the pitch.
4. An "H" following the standard number denotes heavyweight chain. A hyphenated number following the standard number denotes double-strand (2), triple-strand (3), and so on. Thus 60H-3 denotes number 60 heavyweight triple-strand chain.
A typical bicycle chain (for derailleur gears) uses narrow 1⁄2-inch-pitch chain. The width of the chain is variable, and does not affect the load capacity. The more sprockets at the rear wheel (historically 3-6, nowadays 7-12 sprockets), the narrower the chain. Chains are sold according to the number of speeds they are designed to work with, for example, "10 speed chain". Hub gear or single speed bicycles use 1/2" x 1/8" chains, where 1/8" refers to the maximum thickness of a sprocket that can be used with the chain.
Typically chains with parallel shaped links have an even number of links, with each narrow link followed by a broad one. Chains built up with a uniform type of link, narrow at 1 and broad at the other end, can be made with an odd number of links, which can be an advantage to adapt to a special chainwheel-distance; on the other side such a chain tends to be not so strong.
Roller chains made using ISO standard are sometimes called as isochains.
WHY CHOOSE US
1. Reliable Quality Assurance System
2. Cutting-Edge Computer-Controlled CNC Machines
3. Bespoke Solutions from Highly Experienced Specialists
4. Customization and OEM Available for Specific Application
5. Extensive Inventory of Spare Parts and Accessories
6. Well-Developed CZPT Marketing Network
7. Efficient After-Sale Service System
The 219 sets of advanced automatic production equipment provide guarantees for high product quality. The 167 engineers and technicians with senior professional titles can design and develop products to meet the exact demands of customers, and OEM customizations are also available with us. Our sound global service network can provide customers with timely after-sales technical services.
We are not just a manufacturer and supplier, but also an industry consultant. We work pro-actively with you to offer expert advice and product recommendations in order to end up with a most cost effective product available for your specific application. The clients we serve CZPT range from end users to distributors and OEMs. Our OEM replacements can be substituted wherever necessary and suitable for both repair and new assemblies.
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
To be negotiated |
|---|
| Standard Or Nonstandard: | Nonstandard |
|---|---|
| Application: | Motor, Electric Cars, Motorcycle, Machinery, Marine, Toy, Agricultural Machinery, Car, Motor, Electric Cars, Motorcycle, Machinery, Marine, Toy, Agricultural Machinery, Car |
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface, Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Samples: |
US$ 0/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

How do I properly install and align sprocket gears?
Proper installation and alignment of sprocket gears are crucial to ensure smooth and efficient power transmission and to prevent premature wear. Here are the steps to properly install and align sprocket gears:
1. Gather the Required Tools:
Before starting the installation process, gather all the necessary tools, including a torque wrench, measuring tools (calipers or micrometers), leveling tools, and alignment tools.
2. Clean the Components:
Thoroughly clean the sprocket gears and the shafts on which they will be mounted. Remove any dirt, debris, or old lubricant to ensure proper contact between the components.
3. Check for Damage:
Inspect the sprocket gears for any signs of damage, wear, or deformation. If any issues are found, replace the damaged components before proceeding.
4. Ensure Proper Fit:
Ensure that the bore diameter of the sprocket gear matches the diameter of the shaft on which it will be mounted. The fit should be neither too loose nor too tight, and the keyway (if present) should align properly with the key on the shaft.
5. Align Sprocket Gears:
For chain and sprocket systems, align the sprocket gears precisely with each other. The teeth of the driving and driven sprockets should mesh smoothly with the chain. For belt drive systems, ensure the sprocket gears align with each other and the belt tracks properly within the sprockets.
6. Check Axial Alignment:
Ensure that the sprocket gears are axially aligned with each other and perpendicular to their respective shafts. Any misalignment can cause premature wear and noise during operation.
7. Set Tension:
If using a chain and sprocket system, adjust the tension of the chain to the manufacturer's specifications. Proper tension ensures optimal power transmission and extends the life of both the chain and sprocket gears.
8. Lubricate:
Apply the appropriate lubricant to the sprocket gear teeth and the chain or belt as required. Lubrication reduces friction, heat, and wear during operation.
9. Torque Fasteners:
If the sprocket gears are held in place with fasteners (such as set screws or bolts), torque them to the recommended specifications. This ensures that the sprocket gears are securely attached to the shafts and will not slip during operation.
10. Perform a Trial Run:
After installation, run the system at low speed and observe its performance. Check for any unusual noise, vibration, or misalignment. If any issues are detected, stop the system immediately and address the problem.
Following these steps will help ensure that the sprocket gears are properly installed and aligned, leading to reliable and efficient power transmission in your mechanical system.

What are the load-carrying capacities of different sprocket gear configurations?
Load-carrying capacity is a critical factor to consider when selecting a sprocket gear configuration for a specific application. The load-carrying capacity of a sprocket gear depends on various factors, including the material and design of the sprocket, the size and number of teeth, and the type of chain used in conjunction with the sprocket.
Here are some factors that influence the load-carrying capacities of different sprocket gear configurations:
1. Material: The choice of material significantly impacts the load-carrying capacity of the sprocket gear. High-strength materials, such as hardened steel or alloy materials, are often used for heavy-duty applications, as they can withstand higher loads without deformation or failure.
2. Number of Teeth: Sprocket gears with more teeth typically distribute the load over a larger surface area, which can improve their load-carrying capacity. However, an increase in the number of teeth may also lead to higher friction losses in the system.
3. Tooth Profile: The shape of the sprocket gear teeth, such as standard or modified tooth profiles, can affect the load distribution and efficiency of the gear system.
4. Chain Type: The type of chain used with the sprocket gear is crucial in determining the overall load-carrying capacity of the system. Different chain designs, such as roller chains or silent chains, have varying load-carrying capabilities.
It is essential to consult the manufacturer's specifications and engineering data when determining the load-carrying capacity of a particular sprocket gear configuration. Additionally, factors like the speed of operation, environmental conditions, and duty cycle should also be considered to ensure the sprocket gear is appropriately sized for the application.
In heavy-duty and high-load applications, engineers often conduct detailed calculations and simulations to ensure the sprocket gear system can handle the required loads safely and reliably. Proper maintenance and periodic inspections are essential to preserve the load-carrying capacity and extend the life of the sprocket gear system.

What are the different types of sprocket gears and their applications?
Sprocket gears come in various types, each designed for specific applications based on their unique characteristics. Here are some of the different types of sprocket gears and their applications:
- 1. Plain Sprocket: Plain sprockets are the most basic type, consisting of a wheel with evenly spaced teeth. They are commonly used in simple power transmission systems and light-duty applications where precise timing is not critical.
- 2. Idler Sprocket: Idler sprockets are used to guide and tension the chain in a sprocket system. They do not connect directly to a power source but play a crucial role in maintaining proper chain tension and alignment.
- 3. Roller Chain Sprocket: Roller chain sprockets are designed to work with roller chains, which have rollers that engage with the sprocket teeth. They are widely used in applications like bicycles, motorcycles, industrial machinery, and conveyor systems.
- 4. Silent Chain Sprocket: Silent chain sprockets, also known as inverted-tooth chain sprockets, are used with silent chains. These sprockets have specially shaped teeth that engage smoothly with the chain, resulting in quieter operation.
- 5. Engineering Class Sprocket: Engineering class sprockets are heavy-duty sprockets used in industrial applications like construction equipment, mining machinery, and agricultural machinery. They are designed to withstand high loads and harsh operating conditions.
- 6. Taper-Lock Sprocket: Taper-lock sprockets have a tapered bore and are mounted on shafts using a locking bushing. They provide a secure and easy-to-install connection and are commonly used in power transmission systems.
- 7. Rack and Pinion: While not a traditional sprocket gear, rack and pinion systems use a linear rack with teeth that mesh with a pinion gear. This combination is used in applications where rotational motion needs to be translated into linear motion, such as in steering systems and CNC machines.
The choice of sprocket gear depends on factors such as the type of chain or belt used, the desired gear ratio, the amount of load the system will handle, and the specific requirements of the application. Each type of sprocket gear offers unique advantages and is tailored to meet the needs of different industries and machinery.


editor by CX 2023-09-05
China 10B-1 ISODIN industrial transmission conveyor drive link roller chain sprocket bar
Relevant Industries: Developing Materials Stores, Production Plant, Machinery Repair Stores
Customized assistance: OEM, ODM
Material: Stainless steel
Regular: ANSI or ISO
Certification: ISO9001
Merchandise identify: sprockets chain
Software: Transmission Technique
Packaging Particulars: industrial package
Port: ZheJiang
Product parameter
| British Regular Stainless Metal Roller Chain | ||||||||||||
| East Chain NO. | Pitch | Roller diameter | Inner width | Plate thickness | Plate depth | Pin diameter | Pin size | Transvers | Breaking load | Weight per meter | ||
| pitch | ||||||||||||
| P | d1 | b1 | T | h2 | d2 | L | LC | Pt | Q | q | ||
| mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | daN | kg/m | ||
| 06B-two | nine.525 | six.35 | five.seventy two | one.two | 8 | three.27 | 23.4 | 24.four | 10.24 | 1240 | .eight | |
| 08B-2 | 12.7 | 8.51 | 7.75 | one.5 | twelve | 4.forty five | 31.2 | 32.two | 13.92 | 2480 | 1.four | |
| 10B-two | fifteen.875 | 10.16 | 9.65 | 2 | fifteen | 5.08 | 36.one | 37.5 | sixteen.fifty nine | 3100 | one.9 | |
| 12B-two | 19.05 | 12.07 | eleven.sixty eight | 2 | sixteen | five.72 | forty two | 43.six | 19.forty six | 4040 | 2.5 | |
| 16B-two | twenty five.4 | fifteen.88 | seventeen.02 | 4/three | 21 | eight.28 | sixty eight | 69.3 | 31.88 | 5920 | five.four | |
| 20B-two | 31.75 | 19.05 | 19.56 | five/four | thirty | 10.19 | seventy seven.8 | 81.5 | 36.45 | 11000 | 7.two | |
| 24B-2 | 38.1 | twenty five.four | twenty five.four | 6/5 | 36 | 14.63 | one hundred and one.seven | 106.two | forty eight.36 | 17600 | 13.4 | |
| ANSI Normal Stainless Steel Roller Chain | ||||||||||||
| East | Pitch | Roller diameter | Inner width | Plate thickness | Plate depth | Pin Diameter | Pin length | Transvers pitch | Breaking load | Weight for every meter | ||
| Chain NO. | ||||||||||||
| P | d1 | b1 | T | h2 | d2 | L | LC | Pt | Q | q | ||
| ANSI | ISO | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | daN | kg/m |
| Feb-forty | 08A-two | twelve.7 | 7.92 | seven.85 | 1.five | 12 | three.ninety five | 31 | 32.2 | 14.38 | 1920 | 1.2 |
| Feb-50 | 10A-2 | fifteen.875 | ten.16 | nine.four | two | 15 | five.08 | 38.9 | forty.4 | 18.11 | 3040 | 2 |
| Feb-sixty | 12A-2 | 19.05 | 11.nine | twelve.fifty seven | 2.5 | eighteen | five.94 | forty eight.4 | fifty.five | 22.seventy eight | 4340 | three |
| Feb-80 | 16A-two | 25.four | fifteen.88 | fifteen.seventy five | 3 | 23 | 7.94 | sixty two.seven | 64.3 | 29.29 | 7780 | five.2 |
| one hundred-2 | 20A-two | 31.75 | 19.05 | 18.nine | 4 | 30 | 9.5 | seventy six.4 | 80.five | 35.76 | 11800 | seven.six |
| a hundred and twenty-2 | 24A-two | 38.1 | 22.two | twenty five.22 | five | 36 | eleven.1 | ninety five.eight | ninety nine.7 | 45.44 | 16000 | eleven.2 |
| a hundred and forty-two | 28A-2 | forty four.forty five | twenty five.4 | 25.22 | six | forty one.one | twelve.seven | 103.three | 107.9 | 48.87 | 19600 | 15 |
| 160-two | 32A-two | 50.eight | 28.fifty eight | 31.55 | 6 | forty eight | fourteen.27 | 123.3 | 128.one | 58.55 | 25000 | 20.two |
| Short pitchtransmission roller chain | Double pitchtransmission roller chain | Leaf chain | Flank contactslient chain | ||||
| ISO NO. | ANSI NO. | ISO NO. | ANSI NO. | ISO NO. | ANSI NO. | ANSI NO. | |
| 08A | forty | 208A | 2040 | LH0822 | BL422 | SC3 | |
| 10A | fifty | 210A | 2050 | LH0823 | BL423 | SC4 | |
| 12A | 60 | 212A | 2060 | LH571 | BL434 | SC5 | |
| 16A | 80 | 216A | 2080 | LH0844 | BL444 | SC6 | |
| 20A | 100 | 220A | 2100 | LH0846 | BL446 | SC8 | |
| 24A | 120 | 224A | 2120 | LH0866 | BL466 | SC10 | |
| 28A | one hundred forty | … | … | LH 0571 | BL488 | ||
| 32A | a hundred and sixty | LH1571 | BL522 | ||||
| 36A | 180 | LH1571 | BL523 | ||||
| … | … | Double pitchconveyor roller chain | … | … FRB002 Promise Friendship Gifts for Ideal Buddy Luminous Matching Bracelets for Couples Sister Items for Children | Agricultureconveyor chain | ||
| 04B | C208A | C2040 | LH3234 | BL1634 | 81X | ||
| 05B | C208AL | C2042 | LH3244 | BL1644 | 81XH | ||
| 06B | C210A | C2050 | LH3246 | BL1646 | 81XHH | ||
| 08B | C210AL | C2052 | LH3266 | BL1666 | CA550 | ||
| 10B | C212 | C2060 | LH3288 | BL1688 | CA555 | ||
| 12B | C212AL | C2062 | LH4571 | BL2571 | CA620 | ||
| 16B | C212AH | C2060H | LH4571 | BL2571 | |||
| 20B | C212AHL | C2062H | LH4034 | BL2034 | |||
| 24B | C216A | C2080 | LH4044 | BL2044 | |||
| 28B | C216AL | C2082 | LH4046 | BL2046 | |||
| 32B | C216AH | C2080H | LH4066 | BL2066 | |||
| 40B | C216AHL | C2082H | LH4088 | BL2088 | |||
Item demonstrate
Relevant bearing
More solution Organization Profile
Established in May 1979, the yr when China began its open up coverage, we are a mentioned owned complete company combining "industry & investing, technologies & buying and selling". In 2002, our company changed from point out-owned company to private owned organization. Backed up by strong financial electrical power, TS1BC Corrugated bellows coupling Factory Cost Coupling Manufacturer Good Performance versatile shaft connector innovative facilities & technologies, and huge generation functionality of several factories, Xinguang has been developing rapidly in enterprise given that its foundation create lengthy- term and helpful partnership with many customers from most regions of the planet. Now, our staff are more than sixty, in which 50 % of them are engineers. Possibly what helps make us distinct from other buying and selling organizations is that we have a exclusive personnel of each businessmen and experienced mechanical engineers, who have been working in the market for several years. This characteristic of us acts an crucial role in high quality management, cost handle, 1045 steel galvanized motorcycle CZPT and pinion and services performance.
certification
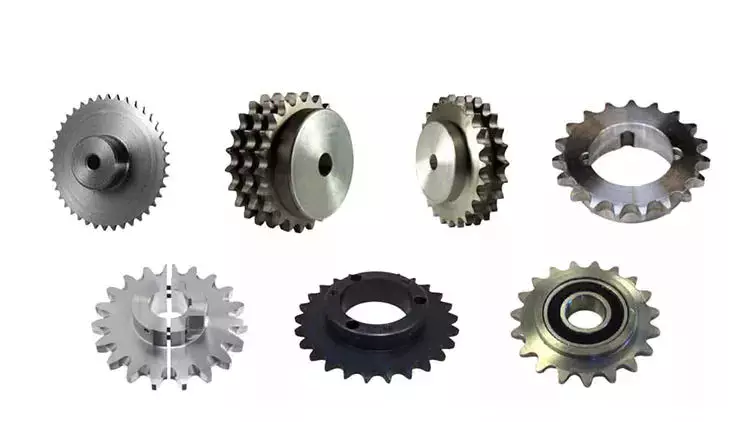

Sprocket Basics
When it comes to sprockets, it's important to understand the basics of design. This includes chain size and number of teeth. The number of teeth will vary depending on the type of chain and application. When determining the number of teeth, the angle between the teeth should be at least 360 degrees.
size
There are many factors to consider when choosing the correct sprocket size. The first thing to do is to determine if the sprocket is a double sprocket or a single sprocket. Also available in a variety of sizes. To determine the exact size, you should measure the distance between the grooves of the sprocket teeth and their opposite tooth slots. The distance between these two points is called the caliper diameter.
The size of the sprockets also varies depending on the type of chain. Large sprockets have arms, while smaller sprockets usually don't. The arms reduce weight and inertia, making them more economical to operate. Some sprockets also have openings, which make them easier to assemble and disassemble. Some sprockets are also plated for a stronger construction. Some sprockets are manufactured with flame or induction hardened parts.
Sprockets are often used in conveyors, pallet conveyors and other conveying systems. The size of the sprocket should match the size of the chain. A caliper will help you determine if the sprocket has worn teeth. Another way to identify worn sprockets is to measure their diameter.
In addition to size, sprockets should have the correct pitch and center distance. This will help keep the roller chain taut. The chain should be clean and properly lubricated. There should be a small gap between the pin and bushing so that oil can pass through the sprocket and chain. In addition to this, the center-to-center distance between the chain and the sprocket should be at least 1.5 times the diameter of the sprocket.
The chain should have at least 17 teeth, which is common in the industry. Having smaller spacing will reduce mechanical losses and noise. However, larger sprocket sizes are best for applications with higher workloads.
Material
Sprockets are mechanical parts that mesh with the chain to move the chain. It is made of metal or reinforced plastic and usually resembles a gear. It is a gear design for a specific type of chain. Most sprocket and chain systems work the same way, although they vary in material and pitch.
There are three basic types of sprockets: single-strand, double-strand, and triple-strand. The length and number of teeth for each type are specified by various standards. For reference, the ISO-DIN standard is shown. Most sprockets are made of alloy steel and are case hardened and tempered in the tooth area. They also have a hub and a key for mounting.
Metal sprockets can be made of steel or aluminum alloys. While steel is a more durable material, aluminum sprockets are more attractive. Steel is the best material for long rides, while aluminum sprockets are better for casual riding.
In addition to automotive and industrial applications, sprockets are used in oil and gas, textile machinery, instrumentation and mechanical transmission. Many types of sprockets are interchangeable with each other. For added protection, they can also be galvanized to prevent rust. The main methods of galvanizing sprockets are hot-dip galvanizing and electro-galvanizing.
Sprockets are usually made of steel or aluminum. Their design is similar to that of gears, although they are more widely spaced than their counterparts. They can also span longer distances than gears, allowing them to be used for power transmission.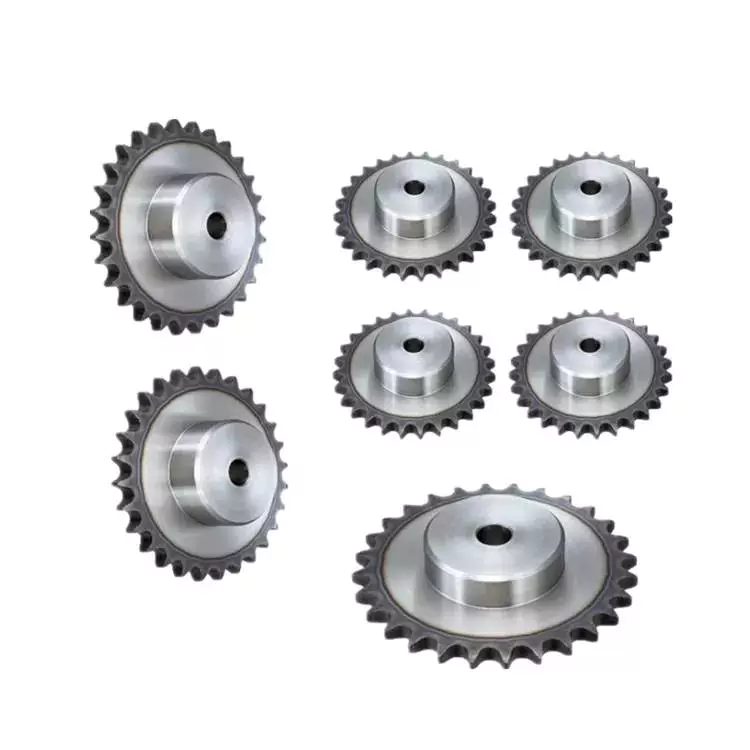
Function
A chain drive is a common type of mechanical transmission in which sprockets are used to help reduce the speed of a moving object. Sprockets can have horizontal, vertical or inclined pitch and are usually used in pairs. The teeth of the sprocket mesh with the rollers on the drive chain, reducing the speed. These sprockets are usually made of metal, but can also be made of plastic or composite materials.
The role of the sprocket is to transmit motion from the output shaft of the engine to the rear wheels. For this, the front sprocket needs to rotate at the same speed as the engine output shaft. It can be mounted either on the drive track or on the front of the vehicle. A third sprocket can be connected to the drive track. In addition, the front sprocket is used to pull the drive chain. This will help transfer power from the engine to the rear wheels, allowing the motorcycle to travel forward. The side plates of the chain also help transmit chain tension.
The bushings are subjected to the tension applied to the chain as it passes through the sprockets thousands of times per minute. This puts pressure on the pin inside the bushing. Additionally, the pins must withstand bending and shearing forces transmitted from the plate to the bushing. The pins must also withstand impact and have high tensile strength. If the pin is worn, it will need to be replaced or repaired.
Sprockets power the chain-driven motion system and carry heavy loads. Proper selection of sprockets can prevent damage to your equipment. To do this, you need to select the appropriate sprocket based on the type of assembly and system specification.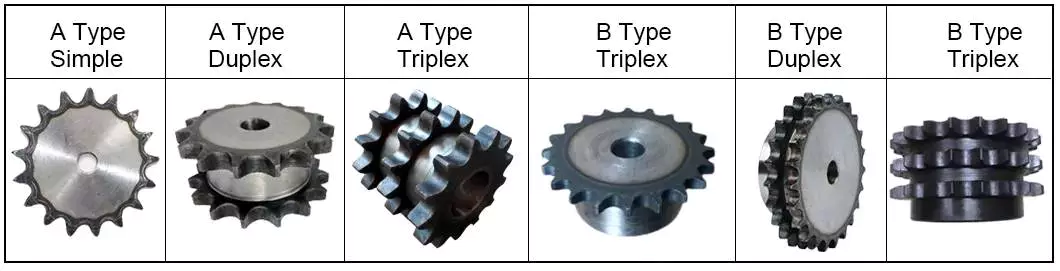
maintain
Sprocket maintenance is an important part of motorcycle maintenance. Failure to do so will result in frequent chain changes and additional costs. Regular maintenance of your chain will help ensure your chain will last 30,000 miles or more. By comparison, a poorly maintained chain only lasts 10,000 miles.
Checking the sprocket is very easy. First, remove the chain and align it. Next, check for any foreign objects. If you see a damaged sprocket, you need to replace it. If you can't replace a worn sprocket, you can buy a new chain. However, the new chain will not last as long as the old one.
Check for signs of rust. Rust can form on the chain due to exposure to humidity and heat. When the pins or rollers get rusted, the seals are damaged. If the pins or rollers are rusted, it's time to replace the chain.
Regular maintenance of the chain is important to prevent kinks and slippage. This can cause excessive wear on the sprockets and chain. If the teeth are worn, the chain will not be able to properly grip the sprocket, resulting in difficult shifting and severe vibration.
If your chain is several years old, it is important to lubricate it every few months to prevent rust. It is also important to clean the chain thoroughly before lubricating to keep it clean and lubricated. Non-petroleum-based cleaners can help remove grit that may have built up. If you use the chain for a long time, you will need to clean it every 300-600 miles.


editor by Cx 2023-06-28
China ASA industrial chain sprocket for conveyor sprocket adapter
Error:获取返回内容失败,
Your session has expired. Please reauthenticate.
How to choose the right sprocket
Knowing the size of the chain is important when looking for the right sprocket. Also, you must know the number of teeth you need and their angle. The angle between the teeth is equal to 360 degrees divided by the number of teeth. This information will help you find the right sprocket for your specific application.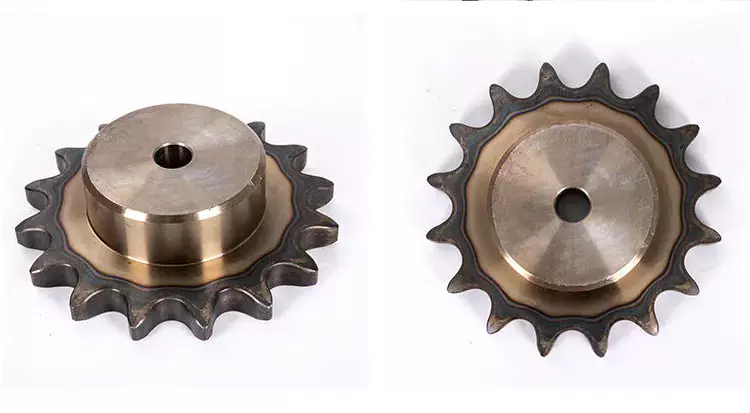
Long Through Hole
Sprockets are critical to the efficiency and uptime of roller chain drives. To ensure your sprocket is installed correctly, it is important to know the dimensions of the sprocket, including its outside diameter, through-hole length, and hub diameter. Pore size is also an important consideration. Most sprockets have a 1/8" bore, while others may have a larger bore.
Sprockets are usually secured to the shaft using ANSI standard-sized keyways and set screws. However, not all sprockets are compatible with all shaft diameters, so it is important to check the keyway size before purchasing.
Sprockets are available in a variety of styles and configurations. Some types of sprockets are welded to a solid hub, while others are bolted or split to the hub. Both types have different adjustments and you can easily change them without disassembling the device. Sprockets can be purchased from many US manufacturers in A, B or C hub configurations. For example, the hub diameter of an A-type sprocket determines its width, while a B-type sprocket has a hole for a bushing.
Sprockets are used in chain-driven motion systems, usually to carry heavy loads. It is very important to choose the right app for the right app to avoid damaging your device. If you're not sure, learn about your system and how it's assembled.
face width
The face width of the sprocket is limited by the meshing clearance with the chain. It does not affect tooth length. The outside diameter of the chain tip may vary depending on the type of tool used. Dimensional tolerances for keyways and set screws are also important.
diameter
One of the most important characteristics of a sprocket is its diameter. The diameter of the sprocket is used as a guide for choosing the proper sprocket size for your bike. Its number of teeth and diameter also affect the size of the chain.
The diameter of a sprocket is a function of its pitch or the distance between the centers of the link hinges. Diameters are in millimeters and expressed in standard ANSI chain numbers. Popular spacing is 3/8" or 1/2".
In order to make the chain drive smoothly, the sprocket and the chain should be properly matched. Incorrect pitch sprockets can damage the chain and shorten its life. Sprockets should provide precise tooth count, consistent pitch, and high wear resistance. It should also be designed to be rigid and impact resistant. CZPT chain suppliers can custom design sprockets in a variety of sizes, pitches, and diameters to suit your needs.
The number of teeth on the roller sprocket is also important. This is because the sprocket is in contact with the chain, causing frictional wear. The teeth on the sprocket can affect the durability of the chain, which is why choosing a sprocket with hardened teeth can change the world.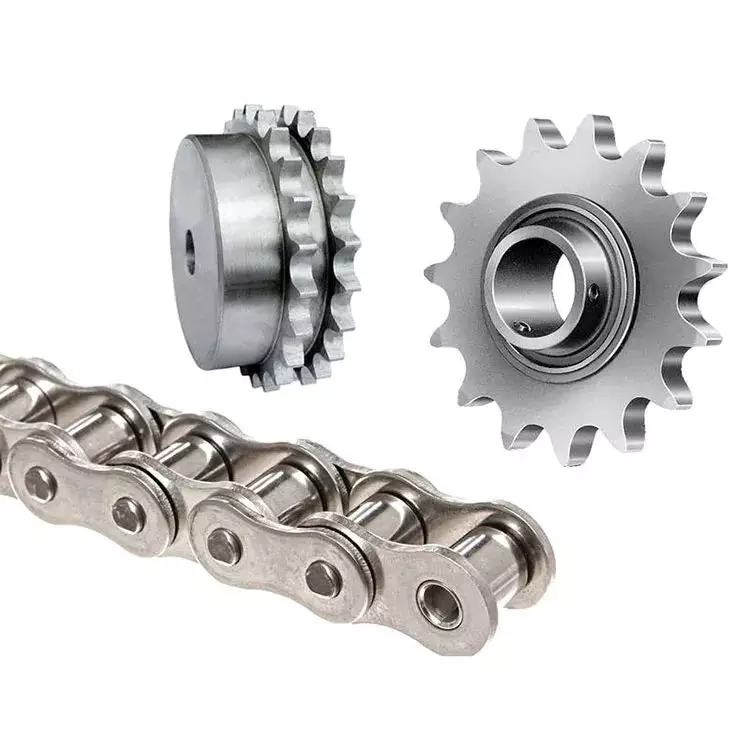
hub type
The hub type of the sprocket is key to proper engagement with the chain. Several options are available. The sprocket hub type is cylindrical and is available in a variety of sizes and styles. Sprockets are usually made of steel or stainless steel.
There are four main types of hubs for sprockets. They come under different names from different manufacturers, but they all share some common characteristics. These include Types A, B, and C. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages. A-Plate sprockets are flat and have no hubs, while B-Hub sprockets are flat with hubs mounted on one side of the plate. C-shaped sprockets extend on both sides of the plate for larger pitch circle diameters and heavier axles.
A sprocket with a large pitch diameter needs a sprocket with a large pitch, and a chain with a small pitch diameter needs a chain with a small pitch. A-type sprockets are smaller and fit more closely to the equipment, while C-type sprockets need to be wider and thicker to carry more weight. Also, the pitch diameter is important because it determines whether the sprocket will fit correctly with the chain.
Steel split sprockets are easy to install and remove. They are held together by bolts on the hub, ranging in pitch size from 40 to 240. They are typically used in applications involving multiple drive shafts.
HZPT ZTB series
ZTB sprockets are an important part of a bicycle chain system. Its uptime is very important to maximize uptime and efficiency. key cSelect sprockets are characterized by size, pitch and bore. MDS accepts sprockets of various bore diameters from 1/2" to 2".
A sprocket is a wheel-like structure with teeth on the end. These teeth interlock with the chain, allowing simple rotational movement of large machines and equipment. ZTB sprockets are an excellent choice for a wide range of applications, including construction and agricultural machinery.
ISO sprockets have a suffix number indicating the number of chains in the chain. For example, 16B-2 sprockets have 1" pitch and dual spools. If you're buying sprockets for your bike, be sure to check the sprocket pitch.
The teeth on the sprocket are responsible for frictional wear, so choosing the right teeth is critical. The right teeth can increase the life of the sprocket and chain. A good sprocket has at least 17 teeth. Sprockets with a higher number of teeth last longer without causing chain slip. Typically, the teeth are the same material as the sprockets, but you can find removable teeth for a more affordable option. The teeth on the sprocket can also be hardened. Induction hardening is the most commonly used process.
ZTB sprockets can be made from many different materials. Some materials are more expensive than others, while others are softer and stronger. If you're not sure which one to buy, try explaining the difference between the different sprockets to the sprocket manufacturer. They should be able to give you details about their interchangeability and quality.
set screw
Set screws are screws designed to hold two or more parts together. There are many different types of set screws, each with a different purpose and design. They usually come in imperial and metric sizes with a hex socket driver on one end and a cup tip on the other. They are made of hardened steel and have a black oxide finish. Some varieties have flanges, while others don't.
Set screws with chain studs can be used in a variety of applications. For example, they can be used in agricultural equipment, heavy equipment and other industries. They come in several different sizes and thread sizes and are available in a variety of designs. Some are specific to the mining industry, while others are more general.
The company also offers custom setscrews, as well as hex, spline, square and socket heads. They have the capability to manufacture fasteners ranging from carbon steel to nickel and silicon bronze. Their products also meet Mil-I-4528 and QS 14000 standards.


editor by czh 2023-02-10